Organic Farming
Home > Organic Farming
Organic
1. Definition
Process (Organic Farming Steps)
1. Soil Preparation – Use of compost, green manure, and crop rotation instead of synthetic fertilizers.
2. Seed Selection – Preference for non-GMO, untreated seeds.
3. Natural Pest & Weed Control – Biological pest control, crop rotation, mulching, and natural repellents instead of chemical pesticides/herbicides.
4. Water Management – Efficient irrigation systems, rainwater harvesting.
5. Harvesting & Storage – Avoidance of chemical preservatives, using clean and sustainable methods.
6. Certification – Compliance with organic standards (e.g., USDA Organic, EU Organic) before labeling.
Benefits
Environmental:
Reduces pollution from synthetic chemicals.
Improves soil fertility and biodiversity.
Conserves water and supports ecosystems.
Health:
Minimizes exposure to pesticide residues.
Often richer in certain nutrients and antioxidants.
Economic & Social:
Supports small-scale farmers.
Encourages sustainable rural economies.
Builds consumer trust in clean food systems.


SUSTAINABILITY
1. Definition sustainability
2. Process in Agriculture
1. Soil Health Management
Crop rotation, cover cropping, reduced tillage, compost use.
2. Water Conservation
Efficient irrigation, rainwater harvesting, preventing contamination.
3. Biodiversity Preservation
Agroforestry, hedgerows, protecting pollinators, planting native species.
4. Climate-Smart Practices
Reduced chemical use, renewable energy on farms, carbon sequestration in soil.
5. Efficient Resource Use
Precision farming (GPS, sensors), balanced fertilizer use, waste recycling.
6. Community & Economic Sustainability
Fair wages for farm workers, supporting local markets, cooperative farming.

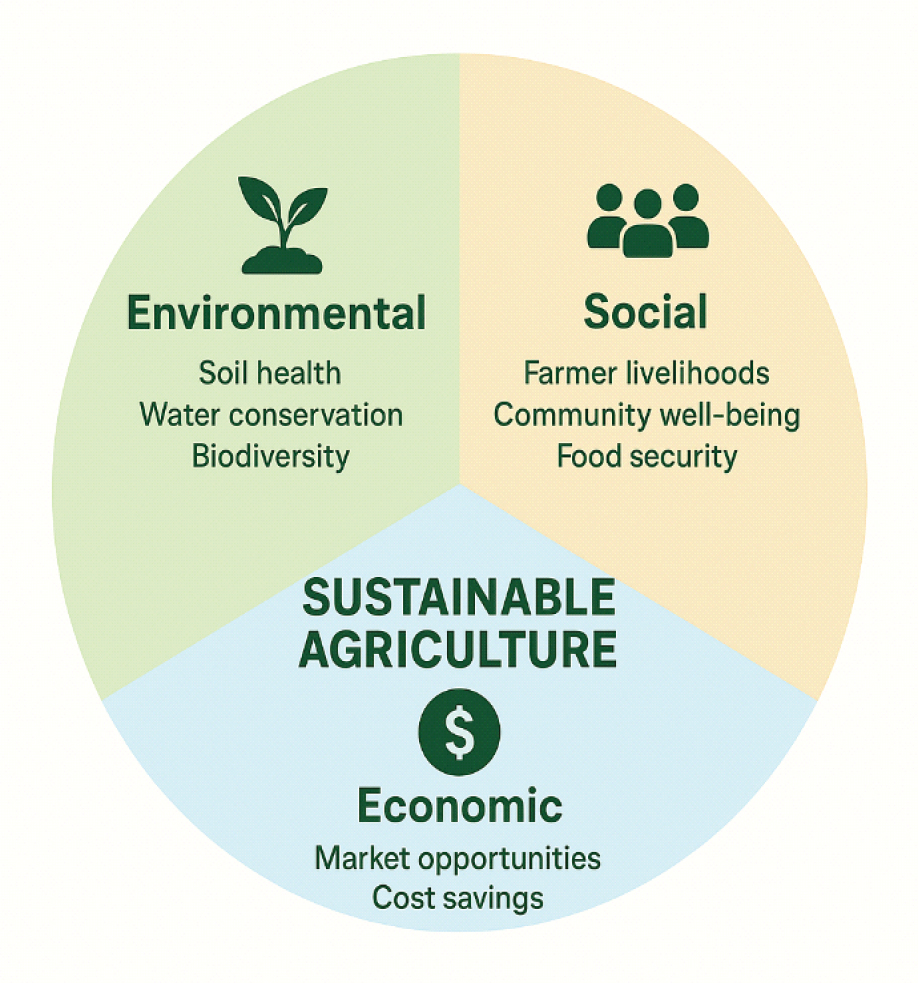
3. Benefits in Agriculture
Environmental
Reduced soil erosion and degradation.
Improved water quality and availability.
Greater biodiversity and ecosystem stability.
Social
Stronger rural communities and farmer livelihoods.
Safer, healthier food for consumers.
Economic
Lower input costs (fertilizers, pesticides, water).
Long-term productivity of farmland.
Market advantage through organic or sustainably certified products.
OUR CERTIFICATE
A product is something made in a factory; a brand is something that is bought by the customer. A product can be copied by a competitor; a brand is unique. A product can be quickly outdated; a successful brand is timeless. verify our products with certificate.











