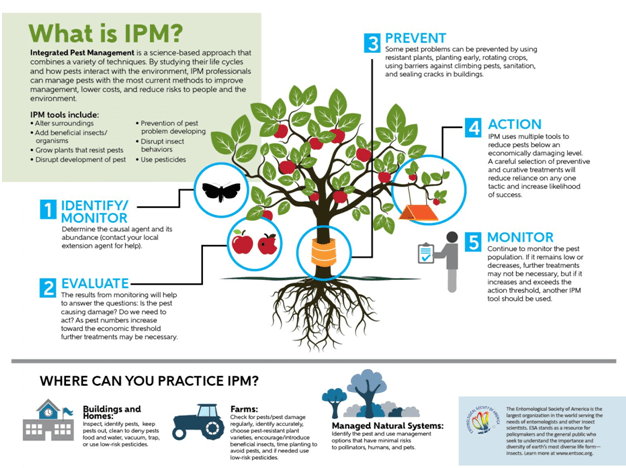
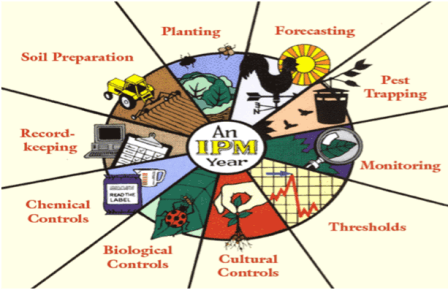
With IPM, you take actions to keep pests from becoming a problem, such as by growing a healthy crop that can withstand pest attacks, using disease-resistant plants, or caulking cracks to keep insects or rodents from entering a building.
Rather than simply eliminating the pests you see right now, using IPM means you’ll look at environmental factors that affect the pest and its ability to thrive. Armed with this information, you can create conditions that are unfavorable for the pest.